If you need to find out the address of a person, having only a VK profile from the data about him, you will need to resort to some methods and tricks that will allow you to successfully identify the place of residence of the wanted person with a certain accuracy.
To calculate a person’s location using VKontakte you need to:
- determine its identification number;
- lure to iplogger or a similar site;
- based on IP information, find information about the country and city of his residence;
- using a special resource (for example wwhois.ru/ip.php) to find a place of residence.
Let's look at each point in detail.
How to find a page by ID in the full version of VK?
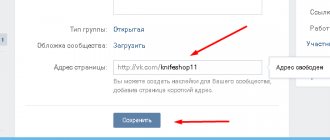
In the full version of the VK website (usually used on a computer or laptop) and in the mobile version of the site (not in the application!) you can do without searching. Just enter the desired id in the browser address bar after /vk.com/ and press Enter.
For example, if we are looking for a person’s page with the following id: id12345678 , then we open VK in the browser and click on the address bar. If the entire address is highlighted, then you need to click again with the left mouse button or the right arrow on the keyboard. We erase the excess if there is anything after /vk.com/. We enter id12345678, and we get https://vk.com/id12345678 . Now just press Enter and the page opens.
The only difference in the mobile version of the site is that the address will not be vk.com, but m.vk.com.
What are ip and id?
If you are not new to the basic theory of social networks, then just scroll through the page to the desired section. But we think that for most readers it will be useful to know the basic principles on which the answers to the main question of the article are based.
So, you've probably often heard terms like ip and id. What is it? Let's start with the IP. This short abbreviation hides the term Internet Protocol, or Internet Protocol. We will not use a complex definition, we will simply explain that ip is a unique address of a node on the Internet, thanks to which nodes communicate with each other with the ability to transmit data. Naturally, the knots are not sea knots. This term simply refers to devices that have access to the network, that is, computers, smartphones, tablets, smart watches, etc.
Knowing the IP address, you can get important information about the device from which you accessed the network. In particular, the country and city, provider, device OS, and browser used are determined. Of course, this is all purely technical data that concerns more the computer than the user. However, in some cases, it is knowledge of the IP address that allows you to resolve serious situations.
Let's move on to the second term - id. This abbreviation is familiar to every person registered on social networks. ID refers to an identification number that is assigned to each user. Here there is already a connection not to the device, but directly to the person. More precisely to his account, because... one person can make several profiles, each of which will have its own individual number.
In general, id is something like ip, but within the framework of specific services. A person’s VKontakte ID, for example, is given upon registration and remains unchanged throughout the entire time they work on the social network. By the way, the situation with IP is different: it tends to change, with the exception of static addresses. But that's a completely different story.
Looking for posts with a specific type of content
And these operators help filter out the most interesting things on a user’s or community’s wall. For example, funny polls from 2006-2009 or tracks in a person’s statuses with hidden audio recordings:
has:poll - polls; has:album - photo albums; has:note - notes; has:photo - photographs; has:audio - audio recordings; has:video - video; has:doc - attached files.
When using the last operator, the feed is filled with posts with GIF files attached. If you need scans of passports, completed tests, samples of completed official documents, then you should look for them on the document search page.
There is also the has:graffiti , which works rather incorrectly, but allows you to find nostalgic greetings from seven years ago.
Application page
We are looking for photos of a specific place on the user’s wall
Just a couple of days ago I came across a situation where a person posted photos from vacation on his wall (without creating an album) and generously diluted them with reposts of quotes about the meaning of life. It was very tiring to watch. What saved me was the ability to filter only posts with photos based on the location on the wall.
On the wall of a user or community (as in the example in the picture), you can enter the geographic coordinates of the desired city and only get photos taken there. For example:
near:57.3,117.2
Unfortunately, the standard “Geolocation” and other advanced search functions do not work on the walls of users and communities.
How to quickly find old correspondence with a user?
Suppose you need to remember what a conversation was about with a person several months or years ago. To do this you need:
1. Open the page with messages, type the name of the desired person in the search and click on it. 2. After that, click Search by conversation . 3. The calendar icon is now visible. It allows you to select messages up to a certain date.
Determining location by IP address
It is worth immediately noting that the described method works extremely rarely, and the sites that are used are of a dubious nature.
If you need a quick way to find a person by ID address in VK (location), then use the IP address for this. IP is also a unique number, but not on a social network, but on the Internet.
The social network carefully hides the data of its users, this is part of its security policy, so you have to use a trick to calculate the IP address:
- You can use an online sniffer, for example, iplogger. You will need to generate a link on the service website, and then convince the desired user to follow this link. After the transition, the site will determine the IP address.
- Another option is to transfer the correspondence to mail.ru - in addition to the text of the letter, the mail will also provide the IP address.
That is, before you can calculate a person’s location, you will need to determine the IP address using your VKontakte ID, and this is a difficult task, especially for an outsider.
To determine the necessary information by IP, specialized services are used, for example, whois. The site will show the city, perhaps an approximate address, but you should not trust this information too much. The address is rarely reliable, and when using VPNs and anonymizers, the real IP is replaced with an IP registered in another city/country.
Why is this necessary at all?
Still, it was necessary to start from this moment: why does it even occur to anyone to define this Internet Protocol? Apparently, there is a great belief that knowing an IP address can seriously help in identifying a specific person. Naturally, you don’t need to find out what IPs your friends have, because... you already know where they live, etc.
Most often, this issue is addressed in situations where scammers contact users through VKontakte. Unfortunately, cases of fraudulent activities through social networks are very common, and some people, despite regular warnings, still fall for the cleverly placed hooks of dishonest citizens.
Alas, even if you manage to calculate the IP, it is unlikely that you will find the person in real life. Most often, the specified IP address does not help track the attacker, because... Most scammers use anonymizers and VPN services. The task of these services is to disable real IP addresses and assign new ones that relate not just to other cities, but to other countries. You've probably encountered them if your provider blocked access to sites. Anonymizers and VPN applications work not only on PCs, but also on smartphones, incl. on iPhone.
So, we draw a conclusion from all of the above. Finding out people's IP addresses only by their VKontakte id is not the best idea. Simply because there is no direct relationship between them. It may also be impossible to find a person by IP address. And there are not many legal ways to do this. Therefore, think about whether you need this at all before you take real action.
Search only among comments
This is how we find mentions of links or words in discussions:
domain:iphones.ru type:reply
And so you can search for the most interesting comments that have collected =>10. =>100, =>1000 likes.
likes:10 likes:100 likes:1000
“Likes” are effective not only for comments, but also for posts, photos, etc. But, unfortunately, they don’t work on the walls of people and communities.
Application page
How to “get” a person onto the Internet: we use Google operators and logic
In the next article in our series of publications dedicated to Internet intelligence, we will look at how Google's advanced search operators allow you to quickly find the necessary information about a specific person.
In the comments to our first article, readers asked for more practical examples and screenshots, so in this article we will have a lot of practice and graphics. To demonstrate the capabilities of “advanced” Google search, the author’s personal accounts were selected as targets. This was done so as not to offend anyone with excessive interest in his private life. I want to immediately warn you that I never set out to hide my presence on the Internet, so the methods described are suitable for collecting data about ordinary people, and may not be very effective for de-anonymizing fake accounts created for one-time events. I suggest that interested readers repeat the examples of requests regarding their accounts and evaluate how easy it is to collect information on them.
Before collecting and analyzing information about a specific person, it is necessary to present the whole picture of what data exists about the person.
Such a map needs to be detailed to the level necessary to solve a specific problem. Any search for information begins with some initial set of data. In our case, this will be the last name, first name and place of work. The rest of the data is somewhere, but we cannot yet link it with the existing data. Therefore, we form hypotheses and test them using search queries.
Sources of information about a person can be:
- himself: accounts on social networks, blog, etc.;
- state: databases of tax authorities, bailiffs, courts, etc. See links in article
- someone else (friends, enemies, media, employer, etc.)
In this article we will consider point 1. – we will calculate the author’s accounts on social networks.
Goal number one: usernames
What is a nickname and how do we choose it?
Nick represents our name on the Internet: we choose it when creating our personal mailbox, and then often use it in various services.
We are not limited in any way when choosing nicknames, but there are favorite algorithms for forming our Internet names:
- Games with your name: last name, first name+last name, first name+year of birth, first name+date, initials;
- Games with the names of your favorite characters (tovbender, napoleon);
- A little about yourself: profession, psychology (coolhacker, murmur);
- Demonstration of hobbies: footballer, boxer;
- “So that no one guesses”: a word in reverse, a Russian word in an English layout, a word in Latin, etc.
If we don't know the nickname, but we know something about the person, we can already make assumptions and check them.
A good way to figure out a user's nickname is to search and analyze his pages on social networks and look for his personal email address.
You can start searching for information about a specific user with a simple query like the following:
john smith chamomile where “daisy” is the name of the company.
At the moment, we must remember that some features of the Google search engine:
- Google reads the query from left to right.
- Google does not distinguish case: "Earth" and "earth" are the same thing for it;
- the length of the request should not exceed 32 words;
- * represents one word in the query;
- you can search for an exact phrase by putting it in quotation marks;
- between the words in the query there is an invisible logical “AND”;
- Google itself can inflect words;
- The “-” operator excludes from output results that contain an expression placed immediately after this operator (necessarily without a space).
- At the top of the results are the pages that Google believes are the most relevant. Nevertheless, this is his guess, since he does not yet know how to read our thoughts;
- To refine the search parameters, you must be proficient in advanced search operators.
Now you can enter a similar query for the author of the article and get a lot of pages, among which should be the pages you are looking for on social networks:
There is a lot of information in the search engine results, and in order to find pages on social networks we will have to review a large number of pages.
Note:
By the way, what should we do if we want to find a person from a certain company, but have forgotten his last name? The asterisk operator can help here:
john*daisy
And if we are looking for a person from Romashka LLC, and there are a million such “Romashka”: JSC Romashka, ANO Romashka, FSUE Romashka, etc.
Option 1. Search for the full phrase “Romashka LLC.”
Option 2. “Minus” unnecessary words: -ANO – JSC –FSUE (but this way you can also “minus” the necessary results, for example, if the page says that our “Romashka” has become friends with the FSUE “Apelsin”.
Now we need to narrow the search results and find the page of the author of the article on the social network VKontakte. This will allow us to determine one of the user's nicknames, and then calculate the email address. To do this, it will be useful to use an operator such as site. It limits the search to a specific domain at any level.
The second link already leads to the page of the author of the article on the VKontakte network. Please note that the author deliberately chose a short nickname: alexdorofeev. Not all Internet resources allow you to set a link to your page yourself; sometimes it is generated automatically, but may contain a nickname taken from an email address.
Using the information and knowledge obtained, we will try to find a similar page on Facebook.
First, for luck, we will enter the following URL in the browser: https://www.facebook.com/alexdorofeev, but, unfortunately, we will see that the page belongs to someone else. Then we’ll use a proven technique and add site:facebook.com to the request.
The search results do not contain a direct link to the profile we are looking for, since the user was vigilant at one time and prohibited “surrendering” his page to search engines
Here it is necessary to make a small digression again and remember how search engines, including Google, work.
What can search engines do and what can’t they do?
Search engines generally work according to the following algorithm:
- Search engine bots crawl sites;
- page content is indexed;
- Based on user requests, links to relevant pages are retrieved.
Search engines cannot:
- index information that can only be accessed by authorized users;
- data that is available after filling out forms, for example, results of downloading from various databases;
- qualitatively extract information from video, photo, audio materials.
Some more nuances:
- context: the search result depends on the user’s request, the history of his previous requests, and the history of page views by other users;
- the search is carried out only in the language in which the user entered his request;
- there is some conflict of interest: search engines make money from advertising that users click on because the pages they need are not at the very top of the search results;
- Censorship is in effect due to the violation of someone’s rights (copyright, right to be forgotten, etc.).
Facebook belongs to the category of Internet resources that do not really favor indexing their site and this is directly reported in robots.txt:
To detect the page of a secretive user on Facebook, we will need to log in to this network and use the built-in search functionality. A link to a user’s page may “leak” and end up in search engine results, but only if the user deliberately published the material under his authorship for everyone to see.
Using the search, the author's page is easily found:
By analyzing the page URL, we can determine another username: adorofeev.
Thus, we have already obtained two nicknames: alexdorofeev and adorofeev. Since there are a lot of users on popular resources, the nickname may differ from what a person really likes to use, since his “native” identifier is already taken by someone. For this reason, the author of the article has a nickname on Habré: alexdorofeeff, although I like adorofeev more.
Knowing the nickname, we can look for more pages potentially associated with the desired person.
Here we will again digress to Google and remember the following points:
- By default, Google looks for an expression (a word or phrase enclosed in quotation marks) in all parts of the page: in the URL, in the title, in the text, in the link text. At the same time, special “advanced” operators allow us to specify exactly where we need the text we are looking for to be. To do this, we need to use the operators: inurl:, intext:, intitle:, inanchor:, as well as their brothers with the prefix all.
- Google understands Boolean expressions and parentheses. AND is a logical “AND”, by default it stands between words separated by spaces in the search line. OR or I – logical “OR”.
- If we use an operator, then after the colon there must be the desired expression without a space.
- The all operators allow them to be applied to a series of expressions after a colon, separated by spaces. For the same tasks, you can use operators without all, but with brackets and logical expressions.
Let's play around with the inurl operator, which searches for pages that contain the desired word in the page URL. Since we already know several nicknames of the author, we can make the following request:
inurl:(adorofeev | alexdorofeeff | alexdorofeev)
In the search results, we will immediately find the pages of the corresponding accounts and some of the pages will belong to the author. Thus, if we have assumptions about the nicknames used, we can get a list of potentially interesting pages at the very beginning of our research.
Closing the topic with nicknames, I would like to draw your attention to services that allow you to quickly find out whether a given nickname is used in a number of popular resources. This way we can find additional pages for a specific person. An example of such a service: https://namechk.com/
How to find out email?
Now, having obtained a set of the user’s favorite nicknames, we can try to find out his personal e-mail. Why is it needed? Sometimes you need to find out whether a particular e-mail belongs to a given person in order to determine the authorship of the letter. E-mail will also be useful for searching for advertisements left by the user on forums, etc.
We know the nicknames, but we don't yet know the domains of the mail services. So let's make some assumptions and check. Since the user is from Russia, it is most likely that he uses one or more of the following services:
- Mail.ru
- Yandex Mail
- Google Gmail
- Rambler mail
Accordingly, we can generate addresses (our hypotheses at the moment) with the nicknames adorofeev, alexdorofeev and alexdorofeeff.
How can we check whether such addresses actually exist? One option: “talk” a little with the mail servers of each service using the SMTP protocol:
Step 1. Find a mail server for a specific domain.
nslookup -type=mx "domain name"
Step 2. Connect to the mail server and simulate the start of sending a message. If the server responds “OK” to the recipient’s name, then there is such an account.
Option 1: email exists.
telnet gmail-smtp-in.l.google.com 25
Option 2: email does not exist.
Email verification
Having determined whether postal addresses exist, we can try to determine whether a specific address is associated with the person we need.
On mail.ru, some users create their own pages, which can be accessed as follows: my.mail.ru/mail/nick/
We “punch” one of the addresses:
You can also view user pages on all Mail.ru projects using a combination of the inurl: and site operators already known to us:
inurl: nickname site: mail.ru
If we know what a person looks like, know his name, or even already found his page on the social network VKontakte (our case), then the task of checking the ownership of a specific email address is greatly simplified. We can use a mechanism to restore access to the page. We need luck: a user with such an address must exist, and post his photo.
Let's check four options for addresses for the nickname “adorofeev” and see that for two addresses there are no pages at all, for one there is a different name:
But for the corresponding address on Gmail.com we find the author’s page:
So, we have figured out the real personal email address.
How to calculate a corporate email address?
Here the situation is much simpler. The thing is that many organizations have their own rules for forming names for email accounts, which are not very diverse: initials + surname, first letter of name + surname, etc. We just need to understand what rule is used in a particular company in order to use it to form the address of the person we need.
We send the following request to Google:
email @domain
Scrolling through the search results, we find the individual addresses of employees and everything becomes obvious.
How to find an Instagram user using geo tags?
Now let's try to figure out the author's Instagram account. First, we check the most obvious options: https://www.instagram.com/adorofeev/, https://www.instagram.com/alexdorofeeff and https://www.instagram.com/alexdorofeev/ We see that these are the wrong accounts .
Having determined that a person works for a specific company, we can search for photos with the corresponding geo-tag. In our case it will be “NPO Eshelon”.
We see that publications with this geo-tag were mostly made by company employees. It is logical to assume that among the subscribers of many employees there should be an account of the author, which we can easily find:
How to use a time machine?
Carrying out a similar analysis regarding the Twitter account, you can find that the author ran the website adorofeev.ru, which is now not available. What to do in this situation? After all, the materials of the disappeared site may be of real interest. In the author’s practice, there was a situation when a similar disappeared site contained published materials from a criminal case, which was interesting to read.
If the site was turned off quite recently, then Google can help us again, offering the cache operator: with which you can retrieve cached pages retrieved by the search engine.
cache:www.adorofeev.ru/
We see that the site was still on on February 5th, but there was nothing interesting about it.
I really want to look into the more distant past - a few years ago. A time machine would be suitable for this and, oddly enough, it exists and is available to any inquisitive user at: https://archive.org/web/
“Punching” the author’s website, you can see that there were some materials there in the past:
Moreover, by selecting certain dates, you can see the site content at a specific moment:
Instead of a conclusion: a few words about process automation and other Google operators
Is it possible to automate the process of finding interesting information using Google? It’s possible, and there are already good attempts: theHarvester script.
It should be noted that Google does not welcome this and is fighting it, so the reliability of the results of using all kinds of scripts will have to be further checked. Even just playing with the completely legal operators that we discussed above, you will constantly see a captcha and will prove that you are not a robot.
The article turned out to be quite lengthy and we did not consider many other Google advanced search operators that can also be useful in Internet intelligence. If the use of operators in a similar vein is interesting, then we will definitely continue this topic in one of the following articles.
Literature
- What’s in my name for you: how to effectively “break through” a person on the Internet?
- Internet intelligence in action: who is Mr./Ms. Habraman?
- Social Media in Identifying Threats to Ensure Safe Life in a Modern City Aleksandr Dorofeev, Alexey Markov, Valentin Tsirlov
- Google Hacking for Penetration Testers, Third Edition 3rd Edition by Johnny Long, Bill Gardner, Justin Brown.
We are looking for all links to the site
If you add this operator to a news search query, you can find all posts that contain a link to a specific site: domain:iphones.ru
Surprisingly, if you just enter iphones.ru
or
https://wwww.iphones.ru
in the advanced search field
Mention the link and set the setting Search any pages from this site , then there are only 404 posts, and with the operator 37,625. And if you just type iphones.ru , then in the results will be a bunch of left-handed iPhone pranks.
Sometimes operators work better than regular advanced search. It is unknown why this happens, but this is confirmed by experiments similar to the example above.
It is convenient to use this operator to obtain a list of articles from a specific site that have been reposted by the person or community being studied. To do this you just need to type domain:iphones.ru
in the search field on the wall.
Application page
How to find mutual friends of two users?
A very convenient service for finding mutual friends and subscriptions. You can find colleagues, classmates, classmates, or a cutting and sewing club that both subjects under study attend. Do you see a new person among your friends? Try to figure out who brought them together or where they could have met.
There you can also find out: the registration date of the page and who is hiding the user in the friends list. If the site asks for your profile information, I recommend logging in under a fake page.
Link to service: 220vk.com